Table 1. Estimated likelihood of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy for case definitions that include symptoms, signs, and nerve conduction studies (recommendations for clinical research studies).
| Neuropathic symptoms | Decreased or absent ankle reflexes* | Decreased distal sensation | Distal muscle weakness or atrophy | NCS† | Ordinal likelihood | | Present | Present | Present | Present | Abnormal | | | Absent | Present | Present | Present | Abnormal | | | Present | Present | Present | Absent | Abnormal | | | Present | Present | Absent | Absent | Abnormal | | | Present | Absent | Present | Absent | Abnormal | | | Absent | Present | Absent | Present | Abnormal | | | Present | Absent | Absent | Absent | Abnormal | | | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent | Abnormal | | | Absent | Present | Absent | Absent | Abnormal | | | Present | Present | Present | Absent | Normal | | | Present‡ | Absent | Present‡ | Absent | Normal‡ | | | Present§ | Present§ | Present§ | Present§ | Normal§ | |
Neuropathic symptoms: numbness, altered sensation, or pain in the feet. NCS, nerve conduction studies. For clinical research studies enrollment should be limited to cases above the bold horizontal line (i.e., ).
*Ankle reflexes may be decreased in normal individuals 65–70 years. † Abnormal NCS is defined in text. ‡ This phenotype is common in “small-fiber” sensory polyneuropathy. Determination of intraepithelial nerve fiber density in skin biopsy may be useful to confirm the diagnosis (see text). |
§This phenotype in the presence of normal NCS is not a distal symmetrical polyneuropathy. This situation is given a negative () ordinal likelihood because the condition cannot be classified as a distal symmetrical polyneuropathy. It is included here to emphasize the importance of including NCS as part of the case definition for clinical research studiesConsensus Process: A formal consensus process (nominal group process)12,22 was used to develop the case definition.
Because there is no single “gold standard” that defines distal symmetrical polyneuropathy, the case definition must account for different levels of certainty for the presence or absence of the disorder. In line with this goal, participants were given several guidelines for developing a case definition. The case definition should: (1) be restricted to “distal symmetrical polyneuropathy”; (2) serve as a definition for the identification of cases in research studies; (3) acknowledge varying levels of diagnostic certainty by including a set of case definitions rank ordered by estimated ordinal likelihood of disease; (4) be simple, practical, and widely applicable by practicing clinicians; and (5) be based, as much as possible, on current best evidence.
Through several face-to-face meetings, electronic mail, and telephone conferences, committee members reviewed the results of the literature review and proposed case definitions of varying ordinal likelihood of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy. Points of agreement and disagreement were identified, discussed, and resolved. The elements of the proposed case definitions were repeatedly tested against the conclusions from the literature review. What evolved from this process was an ordered set of case definitions ranked by likelihood of disease. The essence of the case definition procedure is shown in Tables 1 and 2.
The Quality Standards Subcommittee of the AAN, the Practice Issues Review Panel of the AAEM, and the Practice Guide-lines Committee of the AAPM&R (Appendix 3), reviewed and approved a draft of this paper with the proposed case definition. The draft was then sent to members of the AAN, AAEM, and AAPM&R for further review and then to the journal Neurology for peer review. Boards of the AAN, AAEM, and AAPM&R reviewed and approved the final version of the paper. At each step of the review process, external reviewers’ suggestions were explicitly considered. When appropriate, the expert panel made changes to the document. EVIDENCE
The search yielded 1450 references. After reviewing titles and abstracts, 61 articles were retrieved and reviewed in their entirety. After comprehensive review of these papers, 12 articles attained a grade of Class I, II, or III.2,3,7–10,15,17,18,24–26 These articles serve as the major evidence basis for the case definition and are tabulated in Table 3
Table 2. Estimated likelihood of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy for case definitions that include only symptoms and signs (recommendations for field or epidemiological studies).
| Neuropathic symptoms | Decreased or absent ankle reflexes* | Decreased distal sensation | Distal muscle weakness or atrophy | NCS† | Ordinal likelihood | | Present | Present | Present | Present | ND | | | Present | Present | Present | Absent | ND | | | Present‡ | Absent | Present‡ | Absent | ND | | | Present | Absent | Absent | Absent | ND | | | Absent | Present | Absent | Absent | ND | |
| Neuropathic symptoms: numbness, altered sensation, or pain in the feet NCS, nerve conduction studies. For field epidemiology studies enrollment should be limited to cases above the bold horizontal line (i.e., ). |
*Ankle reflexes may be decreased in normal individuals 65–70 years. † Nerve conduction studies (NCS) are not included as part of the case definitions for epidemiology studies. ND, not done. ‡ This phenotype is common in “small-fiber” sensory polyneuropathy. Determination of intraepithelial nerve fiber density in skin biopsy may be useful to confirm the diagnosis (see text). 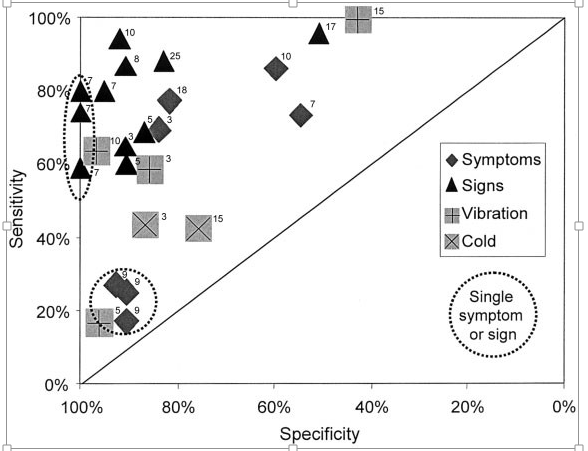
Study Characteristics: Diabetic peripheral neuropathy, which is the most prevalent and rigorously studied type of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy, was the target disorder in most studies. There is a relative lack of high-quality evidence for other varieties of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy. However, three of the studies (25% of the total) focused on cryptogenic sensory peripheral neuropathy. Although limited in quantity, the quality of the articles was high and allowed the development of a case definition for “distal symmetrical polyneuropathy.”
The diagnostic predictors studied varied. Several articles described the diagnostic accuracy of single symptoms including foot numbness, foot pain, and complaints of “sensory alteration.” In addition, some articles measured the accuracy of more complex composite symptom checklists. The accuracy of single examination elements was also determined. These included absent ankle reflexes, decreased distal lower extremity strength, and decreased vibration or cold detection. Some articles also measured the accuracy of composite examinations that included two or more examination elements.
The studies used different reference standards to determine the presence of a symmetric distal peripheral neuropathy. These included nerve conduction studies (NCS), a clinician’s global impression, and composite clinical examination scores.
All studies collected data prospectively. Most were cohort surveys, but some used a case–control design. Four studies described measuring the presence of a polyneuropathy using the reference standard in a fashion that was masked to measurement of the diagnostic predictor. Two studies attained a grade of Class I,8,9 five attained a grade of Class II,2,10,15,18,25 and five attained a grade of Class III.3,7,17,24,26
Diagnostic Accuracy: The diagnostic accuracy of the predictors was determined by calculating their sensitivities and specificities. One way of displaying these data is to plot sensitivities against specificities in a receiver operator characteristics (ROC) curve (Fig. 1).
Predictors encompassing a single specific symptom such as foot numbness have low sensitivity but high specificity for the presence of polyneuropathy. Predictors incorporating the presence of any one of a number of neuropathic symptoms, such as the presence of foot numbness or pain, attain a greater sensitivity but have lower specificity.
Particular single examination findings, such as absent ankle tendon reflexes, have moderate sensitivity and high specificity for the presence of polyneuropathy. When other well-described clinical examination scores.17,25 Notably, simple composite examination scores are as accurate as more complex examinations.
The sensitivities and specificities of quantitative sensory testing (QST) varied widely among studies. These psychophysical tests have greater inherent variability, making their results more difficult to standardize and reproduce. Reproducibility of QST varied from poor to excellent.21,23 For these reasons, QST was not included as part of the final case definition.
| | | | Table 3. Studies meeting inclusion criteria. | | | | | | Article (reference number) | Target disorder | Predictor | Reference standard | Cases | Controls | Design | Spectrum | Masked | Class | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | | 9 | Diabetic PN | Symptom checklist “pain,” “sensory alteration,” “feet numbness” | Clinical exam score 4 | 188 | 400 | Ch | B | Y | 1 | 18 | 91 | | | | | | | | | | | | 26 | 91 | | | | | | | | | | | | 28 | 93 | | 8 | Diabetic PN | 2 of 3: symptoms, abn
temp. sens, 2ankle DTRs | Neurologist clinical evaluation | 15 | 23 | Ch | B | Y | 1 | 87 | 91 | | 10 | Diabetic PN | Symptom
questionnaire, neurologic exam, vibration detection | NCS | 47 | 157 | Ch | N | ND | 2 | 87 | 60 | | | | | | | | | | | | 94 | 92 | | | | | | | | | | | | 64 | 9718 | | 18 | Chronic symmetric PN
in elderly | Neuropathy symptoms | Bilateral impaired sensation,
strength, or
DTR | 11 | 9 | CC | B | Y | 2 | 78 | 82 | | 2 | Diabetic neuropathy | Symptom score,
disability score, vibration detection, cold detection | Two or more abn NCS | 125 | 55 | Ch | N | ND | 2 | 70 | 84 | | | | | | | | | | | | 65 | 91 | | | | | | | | | | | | 59 | 86 | | | | | | | | | | | | 44 | 87 | | 15 | Diabetic PN | Vibration detection threshold, thermal threshold | Clinically overt neuropathy | | | Ch | N | Y | 2 | 100 | 43 | | | | | | | | | | | | 43 | 76 | | 17 | Diabetic PN | Neuropathy exam | Monofilaments vibration detection | 23 | 50 | Ch | B | ND | 3 | 96 | 51 | | 26 | CIAP vs. CIDP | Absent ankle DTRs, biceps and ankle DTRs | Published criteria | 11 | 11 | CC | N | ND | 3 | 100 | 18 | | | | | | | | | | | | 100 | 91 | | 24 | CIAN vs. HSMN | Onset sensory, onset motor,
absent ankle DTR | Family history | 48 | 47 | CC | N | ND | 3 | 60 | 85 | | | | | | | | | | | | 40 | 15 | | | | | | | | | | | | 75 | 11 | | 3 | Diabetic polyneuropathy | NIS-LL | NIS-LL 7 tests | 58 | 137 | Ch | B | ND | 3 | 69 | 87 | | | | Abn ankle DTR, Abn vibration,
One or more abn NCS, Two or more abn
NCS | | | | | | | | 60 | 91 | | | | | | | | | | | | 17 | 96 | | | | | | | | | | | | 93 | 58 | | | | | | | | | | | | 81 | 91 | | 25 | Diabetic polyneuropathy | Exam scoring system | NCS | 49 | 29 | Ch | N | ND | 2 | 88 | 83 | | 7 | Diabetic polyneuropathy | Symptoms, sensory exam,
strength exam, reflexes,
composite exam, screening exam | Mayo criteria | | | Ch | B | ND | 3 | 74 | 55 | | | | | | | | | | | | 74 | 100 | | | | | | | | | | | | 59 | 100 | | | | | | | | | | | | 80 | 100 | | | | | | | | | | | | 80 | 100 | | | | | | | | | | | | 80 | 95 |
Abn, abnormal; B, broad spectrum of patients included; CC, case control; Ch, cohort survey; CIAN, chronic idiopathic ataxic polyneuropathy; CIAP, chronic idiopathic axonal neuropathy; CIDP, chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy; DTRs, deep tendon reflexes; HSMN, hereditary sensory motor neuropathy; LL, lower limb; N, narrow spectrum of patients included; NCS, nerve conduction studies; ND, not described; NIS, neuropathy impairment score; PN, peripheral neuropathy; Sens, sensitivity; Spec, specificity; temp, temperature; Y, yes; , positive; , negative; 2, decreased.

FIGURE 1. The diagnostic accuracy levels of symptoms, signs, or combinations of symptoms or signs (predictors) for the presence of distal symmetric polyneuropathy are expressed. Predictors are plotted according to their sensitivity and specificity. Points plotted near the top of the graph correspond to predictors with high sensitivity for distal symmetric polyneuropathy. Points plotted near the left side of the graph correspond to predictors with high specificity. Thus, points nearest the upper left-hand corner correspond to predictors with the highest diagnostic accuracy (both high sensitivity and specificity) for distal symmetric polyneuropathy. Points falling near the diagonal line correspond to predictors with low diagnostic accuracy. Diamonds: diagnostic accuracy of symptoms; triangles: signs; shaded or X symbols: quantitative sensory tests. Points describing the diagnostic accuracy of a single symptom (e.g., “numbness”) or a single examination finding (e.g., absent ankle reflexes) are enclosed by dashed ovals and circles. Points describing the diagnostic accuracy of more than one symptom (e.g., “numbness” or “pain”) or more than one sign (e.g., “absent ankle reflexes” or “decreased distal sensation”) are not enclosed in dashed ovals and circles. The number just to the upper right of each plotted point indicates the study (reference no.) from which the sensitivity and specificity of that predictor was obtained.
The sensitivities and specificities of quantitative autonomic testing are relatively high for documenting the presence or absence of autonomic dysfunction.3,4 However, these tests are not routinely performed at all medical centers. Because a usable case definition must be based on tests that are simple, practical, and easily available, quantitative autonomic testing is not included as part of the final case definition.
Evidence-Based Conclusions for the Case Definition: Using the definitions for strength of recommendation (Appendix 4) the following conclusions and recommendations can be supported from formal analysis and classification of the literature:
| | 1. | Symptoms alone have relatively poor diagnosticaccuracy in predicting the presence of polyneuropathy. Multiple neuropathic symptoms are more accurate than single symptoms and should be weighted more heavily (Level B). | | | 2. | Signs are better predictors of polyneuropathythan symptoms and should be weighted more heavily (Level B). | | | 3. | A single abnormality examination is less sensitivethan multiple abnormalities in predicting the presence of polyneuropathy; therefore, an examination for polyneuropathy should look for a combination of signs (Level B). | | | 4. | Relatively simple examinations are as accurate indiagnosing polyneuropathy as complex scoring systems; therefore, the case definition can use simple examinations without compromising accuracy (Level B). | | | 5. | There is too much inconsistency among the studies describing the accuracy of QST for its incorporation into the case definition (Level U). |
CONSENSUS-BASED PRINCIPLES
The concept of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy requires a clear definition of “distal” and “symmetrical” in the context of polyneuropathy. Distal refers to those parts most distant from the center of the body. The polyneuropathy must begin in the feet. “Symmetrical” indicates that the symptoms and signs are the same on both sides of the body. Persistent or striking asymmetry of symptoms or signs is inconsistent with the case definition. The case definition must encompass a description of symptoms and signs with an easily recognizable phenotype.
Symptoms: Symptoms may be primarily sensory, primarily motor, or both.3,7–9,17,18,24 Symptoms begin distally in the feet. Sensory symptoms are either persistent or intermittent alterations of sensation initially involving the toes or feet. Occasionally, an isolated digital sensory neuropathy affecting one or more toes may be difficult to distinguish from an early polyneuropathy. The differentiation may be discernible only with time. Frequently described sensory symptoms include numbness, burning, prickling paresthesias, dysesthesias, and allodynia. When motor symptoms are the first manifestation of polyneuropathy, the patient may note weakness in the distal legs. Distal symmetrical polyneuropathy may be asymptomatic, especially in its early stage. An asymptomatic presentation is more likely when positive sensory symptoms, such as dysesthesias or paresthesias, are lacking, or when motor deficits alone are the presenting features. A number of symptom questionnaires and methods for scoring symptoms have been described.2,3,7–10,15,17,18,24–26
Signs: Signs of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy evident on clinical examination may include abnormalities of primary sensory modalities (pain, touch, hot, cold, vibration, and proprioception), the motor system (weakness and atrophy), tendon reflexes (especially depressed or absent ankle jerks), or the autonomic system.
Signs of sensory loss occur in an acral, nondermatomal, nonsingle-nerve distribution. Sensory symptoms and their concomitant signs evolve in a centripetal manner.
Motor signs may include atrophy and weakness of intrinsic foot muscles and associated foot deformities such as hammer toes and pes cavus. Because pes cavus does not always indicate a polyneuropathy, it alone is not sufficient evidence of polyneuropathy. With centripetal progression of motor involvement, weakness of toe dorsiflexion followed by weakness of foot dorsiflexion can be expected.
Tendon reflexes are often depressed or unelicitable. Ankle jerks that are relatively depressed or unelicitable are valuable signs of polyneuropathy; however, the interpretation of such findings requires considerable clinical experience and judgment. In addition, other possible causes of depressed or absent ankle jerks, such as S-1 radiculopathy, focal neuropathies, and age-related decreases, must be excluded.
Signs of autonomic nervous system involvement may also constitute findings consistent with a distal symmetrical polyneuropathy if small fibers are affected. Autonomic dysfunction should begin distally and may include abnormalities of sweating or circulatory instability in the feet.
Electrodiagnostic Studies: No single “reference standard” defines distal symmetrical polyneuropathy. The most accurate diagnosis of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy comprises a combination of clinical symptoms, signs, and electrodiagnostic findings. Electrodiagnostic findings should be included as part of the case definition because they provide a higher level of specificity for the diagnosis.3,5,7,24
Electrodiagnostic studies are sensitive, specific, validated measures of the presence of polyneuropathy.2,3,4,5,7,10,19,20,24 Electrodiagnostic evaluations commonly include both NCS and needle electromyography (EMG). In the diagnosis of polyneuropathy, NCS are the most informative part of the electrodiagnostic evaluation.4,5,7,10,19,20,24 NCS are noninvasive, standardized, and provide a sensitive measure of the functional status of sensory and motor nerve fibers. NCS are also widely performed and suitable for population studies or longitudinal evaluations. The inclusion of NCS in the assessment of polyneuropathy adds a higher level of specificity to the diagnosis.3,5,7,24 For these reasons, NCS are included as an integral part of the case definition of polyneuropathy.
The protocol for performing NCS was determined by the structured consensus process described previously. There are have been many recommendations regarding NCS criteria for the diagnosis of polyneuropathy, but no formal consensus exists. The recommendations that follow are based on electrophysiological principles that combine both the highest sensitivity and specificity as well as the highest efficiency for the diagnosis of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy.
Recommended Protocol for Nerve Conduction Studies: The following set of sensory and motor NCS should be performed if patients are entering a clinical research trial in which NCS will be tracked longitudinally. This protocol includes unilateral studies of sural sensory, ulnar sensory, and median sensory nerves, and peroneal, tibial, median, and ulnar motor nerves with F waves. Other NCS may be necessary as determined by clinical judgment. The minimum case definition criterion for electrodiagnostic confirmation of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy is an abnormality (99th or 1st percentile) of any attribute of nerve conduction in two separate nerves, one of which must be the sural nerve. Electrodiagnostic studies should follow rigorous guidelines such as those set by the AAEM.1 Variables such as skin temperature, age, height, gender, and weight should be measured and accounted for when reporting a NCS as normal or abnormal.1
A simplified NCS protocol may be used for the purpose of defining the presence of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy. However, the abbreviated protocol is not sufficient to determine the subtype or severity of the polyneuropathy. For these purposes, as well as for clinical trials in which electrodiagnostic measures will be tracked serially, the more comprehensive set of NCS is recommended.
The simplified NCS protocol is as follows:
| | 1. | Sural sensory and peroneal motor NCS are performed in one lower extremity. Taken together, these NCS are the most sensitive for detecting a distal symmetrical polyneuropathy. If both studies are normal, there is no evidence of typical distal symmetrical polyneuropathy. In such a situation, no further NCS are necessary. | | | 2. | If sural sensory or peroneal motor NCS are abnormal, then additional NCS are recommended. This should include NCS of at least the ulnar sensory, median sensory, and ulnar motor nerves in one upper extremity. A contralateral sural sensory and one tibial motor NCS may also be performed according to the discretion of the examiner. Caution is warranted when interpreting median and ulnar studies because there is a possibility of abnormality due to compression of these nerves at the wrist or ulnar neuropathy at the elbow. | | | 3. | If a response is absent for any of the nerves studied (sensory or motor), NCS of the contralateral nerve should be performed. | | | 4. | If a peroneal motor response is absent, an ipsilateral tibial motor NCS should be performed. |
Minimal criteria for the electrodiagnostic confirmation of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy are the same as those listed previously.
COMBINING EVIDENCE AND CONSENSUS: CASE DEFINITION OF DISTAL SYMMETRICAL POLYNEUROPATHY
The best approach for defining distal symmetrical polyneuropathy is an ordered set of definitions ranked by likelihood of disease. The likelihood of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy was rated on an ordinal scale from highest likelihood () to lowest likelihood (). Because diagnostic certainty for polyneuropathy follows a continuum of probability, this manner of definition is the most sensible. In each set of case definitions a hierarchy of parameter combinations was established to provide the most relevant combinations for the diagnosis of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy. Combinations of parameters that were considered clinically unusual and not appropriate for research studies were not included. For these reasons not every possible combination of parameters is presented.
The essential characteristics of the case definition are given in Tables 1 and 2. Important aspects of the case definition that warrant emphasis include:
| | 1. | The combination of neuropathic symptoms, signs, and abnormal electrodiagnostic studies provides the most accurate diagnosis of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy (Table 1). | | | 2. | Electrodiagnostic studies are recommended aspart of the clinical research case definition (Table 1) because they are objective and validated tests of peripheral nerve function. Abnormal electrodiagnostic studies increase the likelihood of the presence of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy and provide a higher level of specificity to the case definition. Electrodiagnostic studies should not be used alone to make the diagnosis because their sensitivity and specificity are not perfect. | | | 3. | Electrodiagnostic studies are not required forfield or epidemiological studies (Table 2), but the likelihood of diagnosis must be downgraded accordingly. | | | 4. | For research studies, enrollment should be limited to cases that are most likely to have distal symmetrical polyneuropathy (i.e., those that achieve the highest specificity for the diagnosis). For clinical research studies, this consists of cases with an ordinal likelihood of (Table 1). For epidemiological studies, this consists of cases with an ordinal likelihood of (Table 2). |
LIMITATIONS AND FUTURE RESEARCH
This case definition is heavily weighted toward distal symmetrical polyneuropathy with predominant involvement of “large fibers,” and it is not intended to emphasize the subset of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy termed small-fiber polyneuropathy. Because this type of polyneuropathy may present with only pain and numbness in the feet accompanied by few signs and normal NCS, a formal case definition restricted to small-fiber polyneuropathy is difficult to develop at this time. This is especially true because there is no widely available method to confirm the diagnosis. Determination of intraepithelial nerve fiber density in punch biopsies of skin is a promising technique.11,13,14,16 Inclusion of small-fiber polyneuropathy in a formal case definition must await further studies.
Another limitation of the case definition is that most of the available best evidence is restricted to diabetic peripheral neuropathy. The reason that diabetic neuropathy figures so prominently in the analysis is that it is the most common and rigorously studied variety of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy. The other studies included in the analysis focused on cryptogenic sensory peripheral neuropathy. Thus, some uncertainty exists with respect to the generalization of the case definition for distal symmetical polyneuropathy associated with other etiologies.
The process just described is an attempt to develop formal criteria for a case definition of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy. The principal purpose of the case definition is the identification of cases for clinical research and epidemiological studies. The criteria were formulated using a nominal group process in addition to the best available scientific evidence. Validation and refinement of these criteria in future studies is encouraged. Specifically, additional studies are needed before conclusions can be made regarding the role of QST and skin biopsy in the diagnosis of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy. As quantitative autonomic testing becomes more routinely available, these tests could easily be incorporated into the case definition. Future studies should also compare the criteria delineated in this study with evolving, new criteria. A major aim of the AAN, AAEM, and AAPM&R is that the case definition be modified and refined as new evidence accumulates. APPENDIX 1: GLOSSARY OF TERMS| Predictor (diagnostic predictor): | A symptom, examination finding, or test result potentially predicting the presence of a distal symmetrical polyneuropathy. | | Target disorder: | The condition or disease being sought. In the current context, the target disorder was a specific type of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy (e.g., diabetic peripheral neuropathy). | | Reference standard (“gold standard”): | The test or procedure (or series of tests or procedures) performed to determine the actual presence or absence of a distal symmetrical polyneuropathy. | | Nominal group process: | A formalized, iterative method for achieving consensus from a group of experts that attempts to maximize group reasoning while preserving individual input. | | ROC (receiver operator characteristic) curve: | A standardized graph of sensitivity (true positive rate) by specificity (true negative rate) designed to depict diagnostic accuracy and the trade-off between increasing sensitivity and decreasing specificity. |
APPENDIX 2: DEFINITIONS FOR STRENGTH OF EVIDENCE
Diagnostic Evidence: Class I: Evidence provided by a prospective study of a broad spectrum of persons with the suspected condition. The study measures the diagnostic accuracy of the test using an acceptable independent reference standard for case definition. The test, if not objective, is applied in an evaluation that is masked to the person’s clinical presentations and the reference standard is applied in an evaluation that is masked to the test result.
Class II: Evidence provided by a prospective study of a narrow spectrum of persons with the suspected condition, or by a retrospective study of a broad spectrum of persons with the condition compared with a broad spectrum of control subjects. The study measures the diagnostic accuracy of the test using an acceptable independent reference standard for case definition. The test is applied in an evaluation that is masked to the reference standard.
Class III: Evidence provided by a retrospective study when either the persons with the condition or the control subjects are of a narrow spectrum. The study measures the diagnostic accuracy of the test using an acceptable independent reference standard for case definition.
Class IV: Evidence provided by expert opinion or case series without control subjects. Any study not measuring the diagnostic accuracy of the test using an acceptable independent reference standard for case definition. APPENDIX 3: REVIEWERS
AAN Quality Standards Subcommittee Members: Gary Franklin, MD, MPH—Co-Chair; Catherine Zahn, MD—Co-Chair; Milton Alter, MD, PhD; Stephen Ashwal, MD; Richard M. Dubinsky, MD; Jacqueline French, MD; Gary Friday, MD; Michael Glantz, MD; Gary Gronseth, MD; Deborah Hirtz, MD; Robert G. Miller, MD; David Thurman, MD; and William Weiner, MD.
AANEM Practice Issue Review Panel Members: Richard M. Dubinsky, MD, Chair, Michael T. Andary, MD, MS, Carmel Armon, MD, MHS, MS, William W. Campbell, MD, Joseph V. Campellone Jr., MD, Earl J. Craig, MD, Kenneth James Gaines, MD, James Howard Jr., MD, Robert G. Miller, MD, Atul Patel, MD, Yuen T. So, MD, PhD, and Robert A. Werner, MD, MS.
AAPM&R Guidelines Committee Members: Hilary Siebens, MD, Chair, Greg Carter, MD, David Chen, MD, John Cianca, MD, Gerard Francisco, MD, Deanna Janora, MD, Bharat Patel, MD, Gerard Malanga, MD, Jay Meythaler, MD, JD, Frank Salvi, MD, Richard Zorowitz, MD, and Maury Ellenberg, MD. APPENDIX 4. DEFINITIONS FOR STRENGTH OF RECOMMENDATIONS
| Level A: | Established as effective, ineffective, or harmful for the given condition in the specified population. Usually, a Level A recommendation requires that the pooled result from two or more distinct Class I studies demonstrates a consistent, significant, and important effect. | | Level B: | Probably effective, ineffective, or harmful for the given condition in the specified population. Usually, a Level B recommendation requires that a single Class I study demonstrates a significant and important effect, or the pooled result from two or more distinct Class II studies demonstrates a consistent, significant, and important effect. | | Level C: | Possibly effective, ineffective, or harmful for the given condition in the specified population. Usually, a Level C recommendation requires that a single Class II study demonstrates a significant and important effect, or the pooled result of two or more distinct Class III studies demonstrates a consistent, significant, and important effect. | | Level U: | Data that are inadequate or conflicting. Given the current knowledge the intervention is unproven and an evidence-based recommendation cannot be made. |
DISCLAIMER
The diagnosis of polyneuropathy is complex. The case definition is not intended to replace the clinical judgment of experienced physicians in the diagnosis of polyneuropathy, because none of the criteria have perfect diagnostic accuracy. This statement is provided as an educational service of the AAN, the AAEM, and the AAPM&R. It is based on an assessment of current scientific and clinical information. It is not intended to include all possible proper methods of care for a particular neurological problem or all legitimate criteria for choosing to use a specific procedure. Neither is it intended to exclude any reasonable alternative methodologies. The AAN, AAEM, and AAPM&R recognize that specific care decisions are the prerogative of the patient and physician caring for the patient, based on all of the circumstances involved.
|
|

