Sample Questions
Knowledge-Based Questions
When stimulating a peripheral nerve, increasing the stimulus intensity from maximal to twice the maximal level will:
- A. Decrease the latency due to cathodal migration.
- B. Increase the response amplitude due to cathodal potentiation.
- C. Have no effect on the latency or amplitude.
- D. Decrease the response amplitude due to anodal blocking.
- E. Increase the speed of volume conduction.
In a depolarized segment of axon during the passage of an action potential:
- A. The sodium conductance is increased.
- B. The potassium conductance is decreased.
- C. The membrane potential is -50 mV.
- D. Sodium ions are flowing out.
- E. The calcium conductance is decreased.
A newborn baby (3 kg in weight) being studied for hypotonia had the following conduction study results : peroneal, 30 m/s; median, 28 m/s. Which of the following is the most correct interpretation?
- A. These results are normal for a newborn.
- B. The velocities suggest prematurity.
- C. The baby has a demyelinating neuropathy.
- D. Measurement errors make studies in infants useless.
- E. A neurogenic lesion is present in the arm.
Questions Involving Pictorial Interpretation
The recording electrodes are placed over the extensor digitorum brevis and the 5th metatarsal head and the peroneal nerve stimulated: (a) above the knee, (b) below the fibular head, and (c) at the ankle.
Stimulation is at the time of the arrow shown on the photograph below:
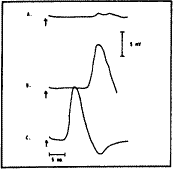
The diagnosis is:
- A. Peripheral polyneuropathy.
- B. Accessory peroneal nerve.
- C. Crossed leg palsy.
- D. Artifact.
- E. Normal.
Which best describes the condition of the nerve in the above image?
- A. Neurapraxia.
- B. Axonal neuropathy.
- C. Neurotmesis.
- D. Generalized demyelination.
- E. Normal.
Questions Involving Video Waveform Recognition or Surface Anatomy
The following questions cannot be answered without viewing the waveform video clips, but are included as representative examples.
Waveform One (vastus lateralis muscle, 30-year-old man, 50 µV/division sensitivity, 10 ms/div sweep speed).
The firing pattern of these potentials is:
- A. Regular and less than 20 per second.
- B. Irregular and less than 20 per second.
- C. Regular and more than 20 per second.
- D. Irregular and more than 20 per second.
- E. Too variable to determine.
These waveforms are:
- A. Fasciculation potentials.
- B. Myotonic discharges.
- C. Positive sharp waves.
- D. Motor unit action potentials.
- E. Normal insertional activity.
The following question is accompanied by a video segment in which the patient is asked to change the angle of his elbow.
The primary muscle responsible for producing this movement is the:
- A. Biceps brachii.
- B. Triceps brachii.
- C. Anconeus.
- D. Pronator teres.
- E. Latissimus dorsi.
